Table of Contents Show
Introduction
Art and technology have always intersected in fascinating ways, but the connection of human emotion with digital data has opened a new frontier in both fields.
As we continue to explore the ways in which technology can represent human experiences, a new question arises:
How can emotional data in digital art give us deeper insights into human behavior?
In this article, we will dive deep into the powerful ways in which emotional data transforms digital art, providing a comprehensive understanding of the science, creativity, and impact behind it.
By converting human emotions into measurable data, artists can create visual masterpieces that reflect the complexities of human psychology.
This intersection doesn’t just serve art—it also furthers research in understanding the core of human behavior.
Capturing the Core of Human Behavior
The foundation of this digital transformation lies in data collection.
But how do we quantify something as abstract as emotion?
Thanks to advancements in behavioral science and technology, human emotions can now be captured using tools like:
1. Biometric sensors
(measuring heart rate, galvanic skin response)

2. Facial recognition software
(detecting micro-expressions)

3. Brainwave activity scanners
(EEG technology)
By combining these tools, researchers and digital artists can transform emotional responses into structured emotional data.
This data is then used to create dynamic visual pieces that are constantly changing in response to the input from the viewers or users themselves.
This process isn’t just about creating visuals; it’s also about unlocking insights into how we, as humans, experience and process emotions.
For example, emotional data in digital art can reveal patterns in behavior, showing how stress, joy, or sadness manifest in artistic expressions.
This provides both artists and scientists with a new avenue to study human emotion on a more objective level.
Transforming Data into Visual Expression
Generative art, a key player in this field, relies heavily on emotional data.
In traditional art, the artist controls every aspect of the creation, but in generative art, the artist designs the system, and the system generates the artwork based on a set of rules.
The rules in generative art often come from human inputs such as emotional data.
When artists feed this data into generative algorithms, it can influence the colors, shapes, and movements in the final artwork.
This creates a symbiotic relationship between technology and emotion.
For instance, digital art installations often use real-time data from visitors; perhaps their heart rate, facial expressions, or even interactions with the artwork itself to generate a unique visual experience.
This allows each individual to leave a personal imprint on the artwork.
In a sense, the art becomes a reflection of their inner state.
This approach is powerful because it not only reflects human emotions in a visual form but also makes the art interactive and deeply personal.
The viewer is no longer just an observer but an active participant in the creation of the artwork.
Art as a Tool for Behavioral Research
Beyond its aesthetic impact, emotional data in digital art has enormous potential as a tool for research into human behavior.
By analyzing how people interact with digital artworks, especially those that respond to emotional data; researchers can gain valuable insights into emotional responses.
For example, a digital art installation that changes based on facial expressions could help researchers understand common emotional responses to specific stimuli.
This has potential applications not only in art but also in fields such as:
- Marketing and consumer behavior (analyzing emotional responses to advertisements)
- Psychology (understanding emotional triggers and coping mechanisms)
- Healthcare (developing new ways to manage stress, anxiety, and depression through interactive art)
By examining the patterns in emotional data, researchers can also study how emotions influence decision-making, social interaction, and even physical health.
Emotional data in digital art offers a non-invasive, engaging way to explore these complex subjects, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of human behavior.
Innovating at the Intersection of Art and Data
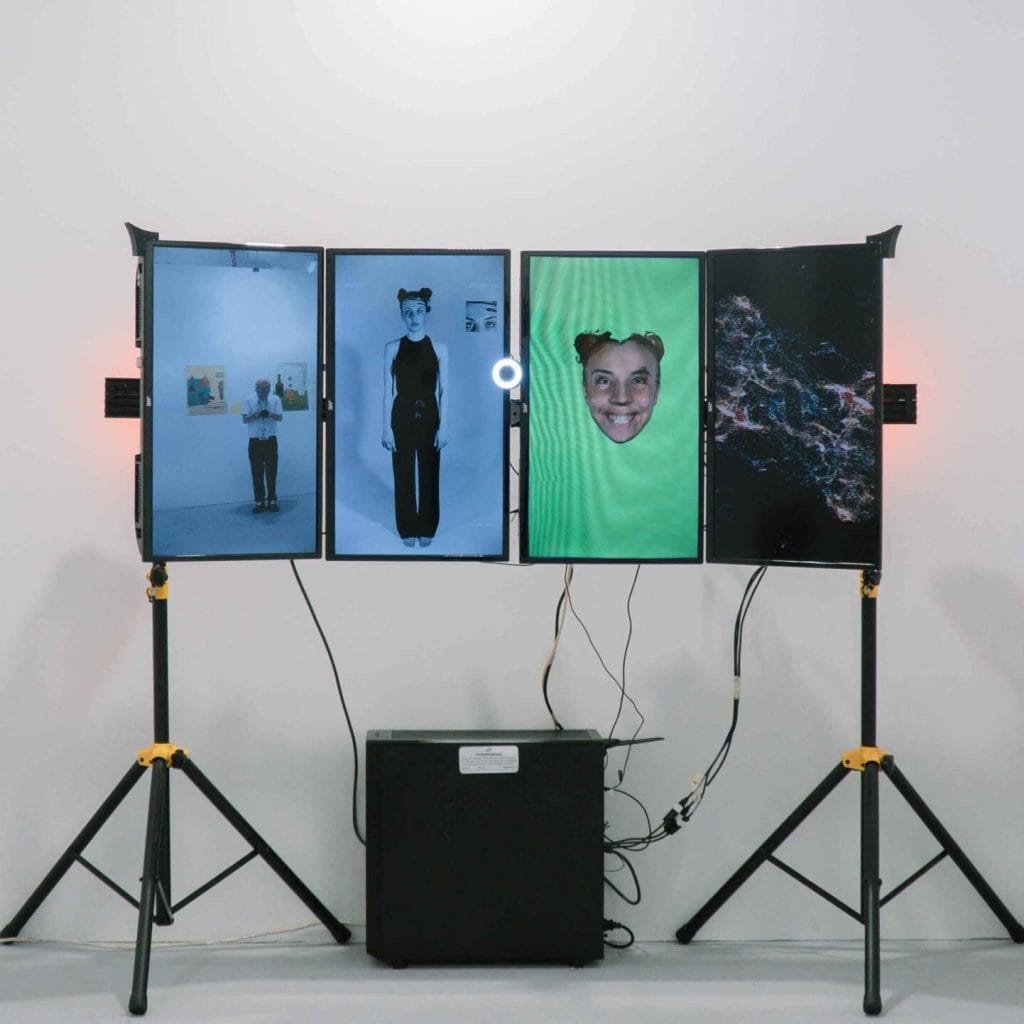
My artistic research at Saphire Labs, leverages emotional data to develop digital art installations.
The lab focuses on using emotional data in ways that enhance viewer interaction and understanding of their own emotional states.
As emotions change, so does the artwork, offering viewers an opportunity to reflect on their own emotional states in a way that’s both immersive and insightful.
This real-time feedback loop transforms the viewer’s emotions into an evolving artwork, thus allowing emotional data in digital art to serve as both a mirror and a meditation tool.
This approach has been especially powerful in therapeutic settings, where art becomes a way for individuals to visualize and process their emotions.

The Future of Emotional Data in Digital Art and Society
The impact of emotional data in digital art is far-reaching.
As technology continues to evolve, artists are beginning to explore more advanced ways to visualize emotions and behaviors, leading to new opportunities in both the artistic and scientific worlds.
Looking ahead, one of the most exciting areas for growth is the potential for AI-generated art.
As AI becomes more sophisticated, it may be able to interpret emotional data even more precisely, creating art that not only reflects but also predicts emotional states.
This could have implications for fields like psychology, where AI-driven art might one day be used as a therapeutic tool.
Moreover, this intersection between art and data raises important ethical questions.
As more personal data is collected and visualized, how do we ensure that it’s used responsibly?
Protecting privacy and ensuring that emotional data is used ethically will be a key consideration as the field moves forward.
Conclusion
Emotional data in digital art is not just about creating beautiful visuals; it’s about understanding humanity on a deeper level.
By combining technology, art, and data science, artists and researchers are opening new doors into the human experience.
These advancements offer both a richer understanding of ourselves and an exciting new avenue for creative expression.
The powerful ways in which emotional data transforms art demonstrate that the boundary between art and science is more fluid than ever.
As we move into the future, the ability to use art as a tool for understanding human behavior will only become more critical, offering new insights into how we think, feel, and interact with the world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is emotional data in digital art?
Emotional data in digital art refers to the collection of human emotions (via biometric sensors, facial recognition, or brain activity) and converting this information into a digital form that artists can use to create dynamic and responsive artwork. This art often reflects or responds to the emotional state of the viewer or participant.
2. How do artists collect emotional data for their artwork?
Artists collect emotional data using various technologies such as biometric sensors (measuring heart rate, skin response), facial recognition software (detecting emotions through expressions), and EEG (brainwave activity monitoring). This data can then be fed into algorithms that influence or generate art.
3. How does emotional data influence generative art?
In generative art, emotional data influences the algorithm’s output. For example, an individual’s emotions may change the color, shapes, or movement in a piece of digital art, creating a personalized and unique visual representation that evolves based on real-time emotional input.
4. What role does emotional data play in behavioral research?
Emotional data can help researchers study human behavior by tracking how emotions change in response to various stimuli, such as interactive digital art. It offers insights into emotional responses, decision-making processes, and psychological patterns, which can be applied to fields like psychology, marketing, and healthcare.
5. Can emotional data in digital art help in mental health therapy?
Yes, emotional data-driven digital art has potential therapeutic applications. By visualizing emotions in real time, it can help individuals become more aware of their emotional states, leading to improved emotional regulation. In therapeutic settings, it can be used as a tool to manage stress, anxiety, or depression.
6. What are some examples of emotional data in digital art installations?
Some examples include art installations that respond to the viewer’s emotional state by changing visuals based on heart rate or brain activity. For instance, interactive digital walls that change color based on a viewer’s stress levels or immersive environments that adapt based on facial expression recognition.